Accessible MS Word Docs
Accessible Microsoft Word Documents
Microsoft Word provides various options for including accessibility information into the document to support individuals using assistive technologies. Such information also provides improved accessibility when converting the document into other formats (e.g., tagged PDF, EPUB, DAISY, etc.). Microsoft Word document accessibility can be improved for the following content items:
Document Headings
Styles in MS Word 2010
- From the Home tab in the top ribbon, select the appropriate heading
- Headings should follow a logical structure that identifies content based on its importance in the document.
- Maintain a sequential organization for headings, e.g., avoid having a heading 2 before a heading 1.
- You can change the formatting of a heading by using the formatting palette.
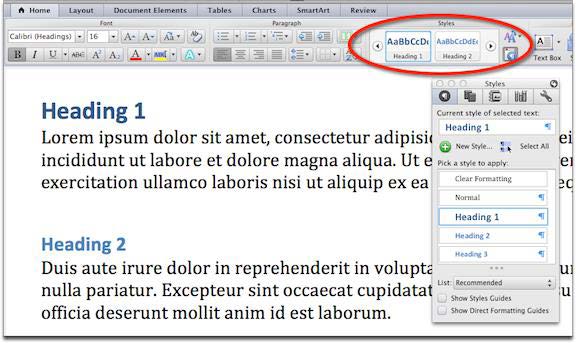
- From the Home tab in the top ribbon, select the appropriate heading level. You can also set headings from the Styles formatting
- Headings should follow a logical structure that identifies content based on its importance in the document.
- Maintain a sequential organization for headings, e.g., avoid having a heading 2 before a heading 1.
- You can change the formatting of a heading by using the formatting palette.
Descriptions for Images
Image descriptions in MS Word 2010
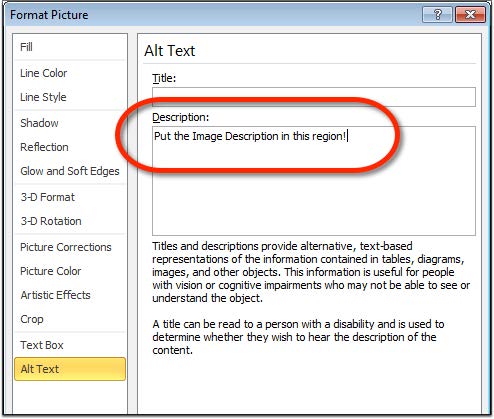
- From the Insert ribbon, choose Picture and select the desired picture to add to the
- Right-click on the image and choose Format Picture. In the left-side settings, choose Alt
- Enter the description of the image in the Description region. Leave the Title field
- The image description should focus on the purpose and/or content of the image in the document.
Image descriptions in MS Word for Mac 2011
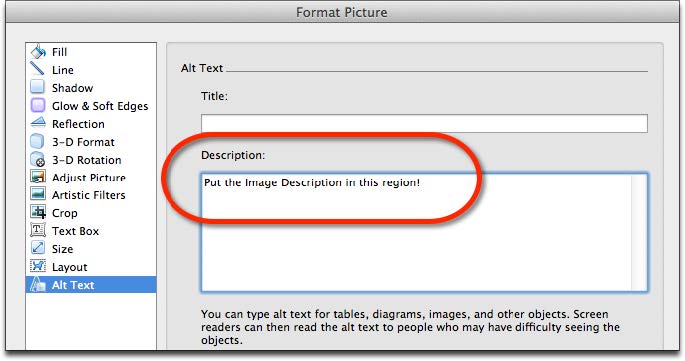
- Choose Insert > Photo > Picture from File… and select the image to add to your document.
- Right-click on the image and choose Format Picture. In the left-side settings, choose Alt Text.
- Enter the description of the image in the Description region. Leave the Title field empty.
- The image description should focus on the purpose and/or content of the image in the
document.
Tables for Data
| City | State | Zip Code |
|---|---|---|
| San Jose | California | 95101 |
| San Francisco | California | 94126 |
| Denver | Colorado | 80210 |
The first row of the table consists of the column headers. These help “define” the category of information for the data in that column. In MS Word, it is possible to identify the headings such that when the data table is interpreted by assistive computer technologies and read to the student, the information in the cells below each heading will have meaning and context.
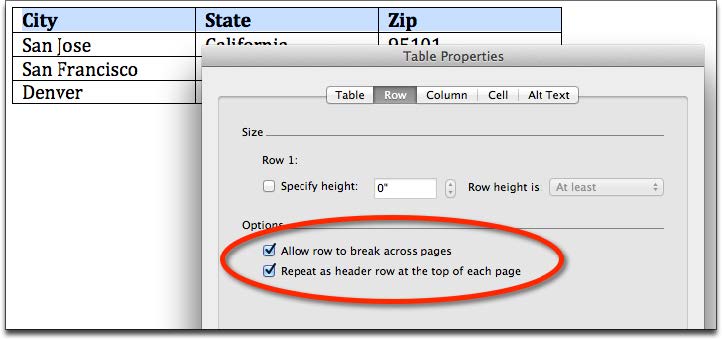
- Create your data table using the Insert Table option under Table on the menu
- Select (highlight) the first row of the data table with your column
- Right click in the highlighted area and choose the Table Properties
- Under the Row tab, check the checkbox Repeat as header row at the top of each page.
- Choose OK and return to the MS Word document.
At this time, there is only support for adding table heading information for table column headers, not row headers. This does not mean you are limited as to the types of tables you can create, rather this is a limitation in MS Word.
Multiple Columns
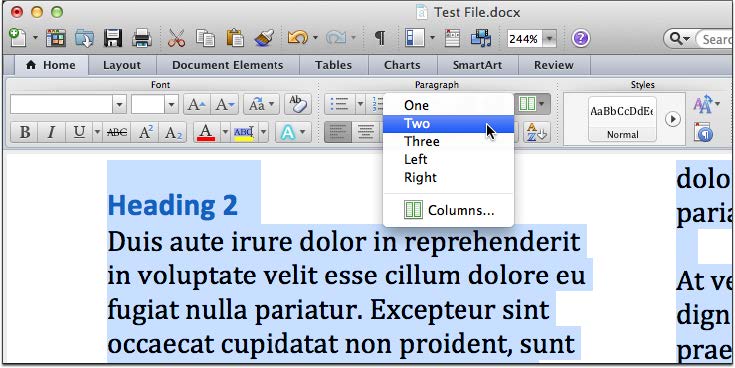
- Select the text you wish to change from a single column to a multi-column
- Choose “Format” on the menu bar and select “Columns…”. Alternatively, choose the Column tool in the Home
- Select the number of columns or set your specific spacing requirements. Return to the document to review the new layout.
Document Hyperlinks
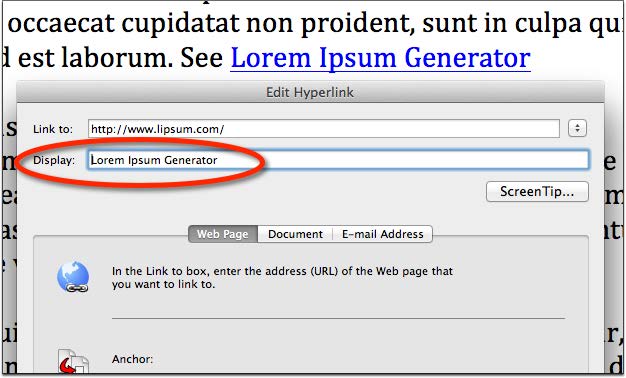
- Right-click on the hyperlink text in the document and choose Edit Hyperlink, or press Ctrl+K (Mac: Cmd+K).
- In the field “Display” (or “Text to Display” for MS Word 2010) enter the correct text
- You can include both the text description and full URL if you prefer. Using the full URL is helpful for when the document is printed.
Mathematical Content
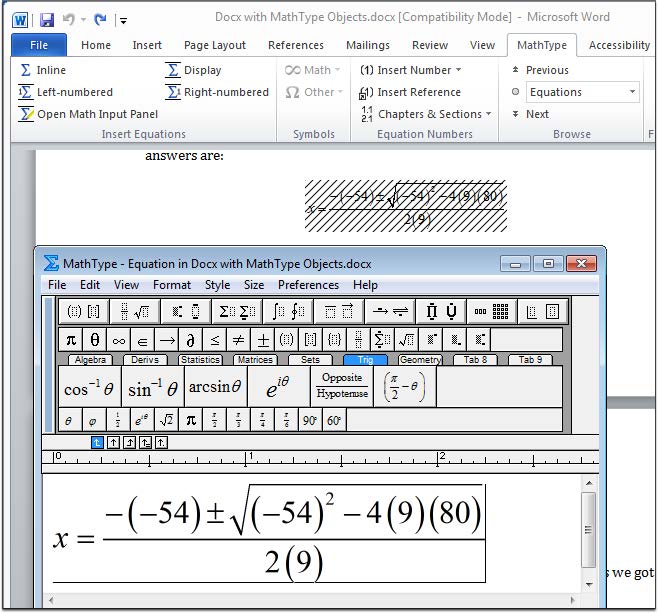
Key Points
- You will need to install the MathType Equation Editor from Design Science to support accessible math equations in MS Word documents. MathType is available for both the Mac and Windows platform.
- With MathType installed, you can enter equations using the MathType Equation Editor or by adding LaTeX. If using LaTeX, you will need to convert all equations to MathType
- MathType should be used for equations and not for entering text information. Avoid using MathType for formatting
- At this time, documents must be saved as DOCX in order to be converted into alternate formats using SensusAccess (e.g., DAISY+Math, EPUB 3, ).
- We are investigating additional input formats, including LaTeX and MathML, to support conversions into alternate document formats. Thank you for your patience.
Provided courtesy of Sean Keegan.